Influence of the properties of the heat affected zones of longitudinal welds on gas pipeline integrity
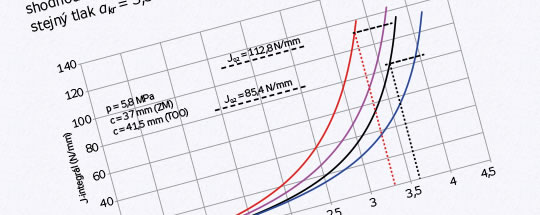
The contribution outlines the results of measurements of the mechanical and fracture mechanics properties of the base metal and the heat affected zone of longitudinally welded Ø 720/8 mm pipes made of 17GS steel under GOST 19281 specifications (equivalent to S355J2G3).
The pipeline transported crude oil from Russia to the Ventspils terminal (Latvia) on the Baltic Sea coast in the past. Now, following pipeline revalidation, it is expected to be reliably used for the future.
The identified values of mechanical and fracture mechanics properties have shown that the heat affected zone does not have to be the weakest area of a weld in terms of resistance to fatigue crack growth and to fracture, as is generally assumed in technical practice; on the contrary, the fracture properties of the heat affected zone can surpass those of the base metal.
This is borne out by the heat affected zone’s higher resilience to fracture than that of the base metal, all other strength properties being virtually the same, and also by the lower value of the exponent in the Paris equation.
Read more in the article Influence of the properties of the heat affected zones of longitudinal welds on gas pipeline integrity (PDF, Czech language, 1165 kB).
