Preventing the formation of flammable hydrocarbon mixtures through inerting
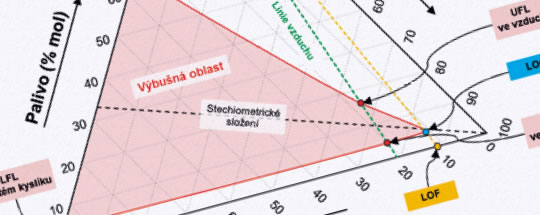
For a case of nitrogen inerting of REB crude vapours, the conducted experiments examined a the minimum requirement for purging nitrogen purity using a relationship between the MAI parameter and absolute initial pressure ranging between 1 bar and 26 bar (25 °C).
The results have confirmed that the nitrogen units operate safely below the limiting residual oxygen content (above the limiting purging nitrogen purity) in the examined range of operating pressures.
Direct purging of gas pipelines using air carries an explosion hazard due to the formation an explosive mixture. The situation get is even more complicated in case of purging a pipeline carrying rich gas due to hydrocarbon condensate separation. Analogically, oil and other petroleum products displacement operations are also challenging as regards safety.
The indirect purging method replaces air with inert gas (typically nitrogen) in order to reduce the explosion hazard (mandatory in case of pipelines transporting flammable liquids).
For this method purpose, CEPS has developed and operates nitrogen units producing a nitrogen inerting mixture with a low content of residual oxygen. These units bring more convenience as regards flexibility, off-road mobility and operating economics compared with conventional liquid nitrogen tank trucks.
For a case of nitrogen inerting of REB crude vapours, the conducted experiments examined a the minimum requirement for purging nitrogen purity using a relationship between the MAI parameter and absolute initial pressure ranging between 1 bar and 26 bar (25 °C).
The results have confirmed that the nitrogen units operate safely below the limiting residual oxygen content (above the limiting purging nitrogen purity) in the examined range of operating pressures.
Read more in the article Preventing the formation of flammable hydrocarbon mixtures through inerting (PDF, Czech language, 1245 kB).
